How Many Valence Electrons Are in Alkali Metals
Oxygen is in the 16th period. When this happens the atom is referred to as an ion and since it would have a positive charge it is called a cation.

Graduation Of Atomic Radius Property In The Periodic Table Science Online Electron Affinity Ionization Energy Electron Configuration
One loosely bound valence electron.

. Many elements have a common valence related to their position in the periodic table and nowadays this is rationalised by the octet ruleThe GreekLatin numeral prefixes mono-uni- di-bi- tri-ter- and so on are used to describe ions in the charge states 1 2 3 and so on respectively. If we subtract 10 from 16 we get 6. The alkali metals form many intermetallic compounds with each other and the elements from groups 2 to 13 in the periodic table of varying stoichiometries.
Boron group Group 13 III 3. Frequently Asked Questions FAQs. However the 1s sublevel has.
In general the transition metals with their valence-level d electrons are stronger and have higher melting points. Concepts to Understand Valence Electrons Electrons are tiny subatomic particles that revolve around the nucleus in energy shells called orbits. Alkali metals have only 1 ionic charge in their compounds when alkaline earth metals have 2 ionic charges in their compounds.
However the lost electrons of alkali metals will also be transferred to the Os sites and provide more shared electron pairs for N and Os sites thus promoting the adsorption of NO. As you keep counting the columns youll know how many electrons are in the. Nonetheless there is wide variation in the densities of metals.
Typically form colored salts. If you look at the periodic table and at the period numbers that is the number of valence electrons. As electrons have a charge of -1 losing an electron causes the atom to have a charge of 1.
Valence electrons are the electrons contained in the outermost shell. Therefore oxygen has six valence electrons. Every element in the second column group two has two electrons in the outer shell.
Less dense than other metals. Have high melting and boiling points. Every element in the first column group one has one electron in its outer shell.
Moreover alkali metals are very soft and they can be cut with a sharp knife. Since Hydrogen H has 1 valence electron it is usually placed in the alkali metal group as that electron is found in the s sublevel. Alkaline earth elements can donate both valence electrons to.
Halogens Group 17 VII 7. How do you find the valence electrons. Some of these have ionic characteristics.
Oxygen group Group 16 VI 6. D-block elements behave in a manner that is somewhere between that of highly reactive electropositive alkali metals and the covalent compound forming elements which is why they are called transition elements. 81 such as the sodium amalgams with mercury including Na 5 Hg 8 and Na 3 Hg.
Metals are electron donors metals loses donates electrons The elements which show this type of nature nature of losing electrons are known as metals. 3 The β-MnO 2 1 1 0 surface has a good ability to catalyze the NH 3 dehydrogenation but may lead to a large amount of N 2 O generated in the presence of many N atoms on the surface. Those outer electrons are also called valence electrons.
Learn more about a valence electron including its. Carbon group Group 14 IV 4. Valence electrons located on an atoms outermost shell affect how an atom will behave with other atoms.
Now in the Periodic table these metals are found on the left side. Like all alkali metals lithium is highly reactive and flammable and is stored in mineral oil. They are the electrons involved in chemical bonds with other elements.
How many valence electrons are in each shell. Element 118 should be a noble gas as 118 electrons would arrange to fill 7p sublevel 7. Noble gases Group 18 VIII or 0 8.
Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element. If the number is larger than 10 subtract 10 so you get two valence electrons. Youll find more specific groups like transition metals rare earths alkali metals alkaline earth halogens and noble gasses.
Alkaline earth metals Group 2 II 2. Hence alkaline earth metals have more density and harder than alkali metals. Make an argument for placing hydrogen in the halogen family rather than the alkali metals.
Nitrogen group Group 15 V 5. Click on an element to read about the chemical and physical properties of the group to which that element belongs. Groups in the Periodic Table of Elements.
These subatomic particles carry a negative charge of 1602 times 10 19 Coulombs. Chip Nataro chemistry professor at Lafayette College in Easton Pennsylvania. However some atoms can be stable with eight electrons even though their valence electrons are in the 3n shell which can hold up to 18 electrons so it depends on the element.
Most elements that are essential in chemistry require eight electrons in each shell to be stable. Lithium Li is the least dense. Comparatively alkali metals are more reactive than alkaline earth metals.
Naturally occurring potassium is composed of three isotopes of which 40K is radioactive. Polyvalence or multivalence refers to species that are not restricted to a specific. And all alkaline earth metals have two outer electrons.
Have valence electrons in their two outermost and shells. It is a soft silvery-white alkali metal. In the periodic table potassium is one of the alkali metals.
The majority of metals have higher densities than the majority of nonmetals. Taking the alloys with gold the most electronegative of metals as an example NaAu and KAu are. All of the alkali metals like to give up their single valence electron says Dr.
All of the alkali metals have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell which is easily removed to create an ion with a positive charge a cation which combines with anions to form salts. Density generally increases from magnesium to radium while calcium has the lowest density among the alkaline earth metals. In addition due to the presence of two valence electrons atoms have stronger metallic bonding.
Alkali metals Group 1 I 1. Lithium is a chemical element with atomic number 3 which means there are 3 protons and 3 electrons in the atomic structureThe chemical symbol for Lithium is Li.

Alkali Metals Metallic Bonding Relatively Weak Because There Is Only One Valence Electron Meta Periodic Table Of The Elements Periodic Table Study Time Table

Ptable Interactive Periodic Table Of Elements Interactive Websites Periodic Table Interactive

Element Infographics The Alkali Metals Poster By Compound Interest Alkali Metal Chemistry Lessons Element Chemistry

Halogen Elements List And Facts Electron Configuration Electron Affinity Nuclear Medicine

Science Coverage Valency Of Lithium How Many Valence Electrons Do Electron Configuration Electrons How To Find Out

Science Coverage Valency Of Cesium How Many Valence Electrons Doe Element Chemistry Electron Configuration Electrons

Numbers In Parentheses Are Atomic Mass Numbers Of Most Stable Isotopes Periodic Table Of The Elements Plate Tectonics Periodic Table

How Many Valence Electrons Does Aluminum Al Have In 2022 Electrons Electron Configuration Ionic Bonding

How To Write Electron Configurations For Atoms Of Any Element Electron Configuration Periodic Table Chemistry Help

Periodic Table Groups And Periods Periodic Table Periodic Elements Octet Rule

A Basic Version Of The Periodic Table With The Updated Symbols For Elements 113 To 118 Periodic Table How To Memorize Things What Is Matter

File Electron Shell 051 Antimony Svg Wikimedia Commons Electrons Electron Affinity Shells
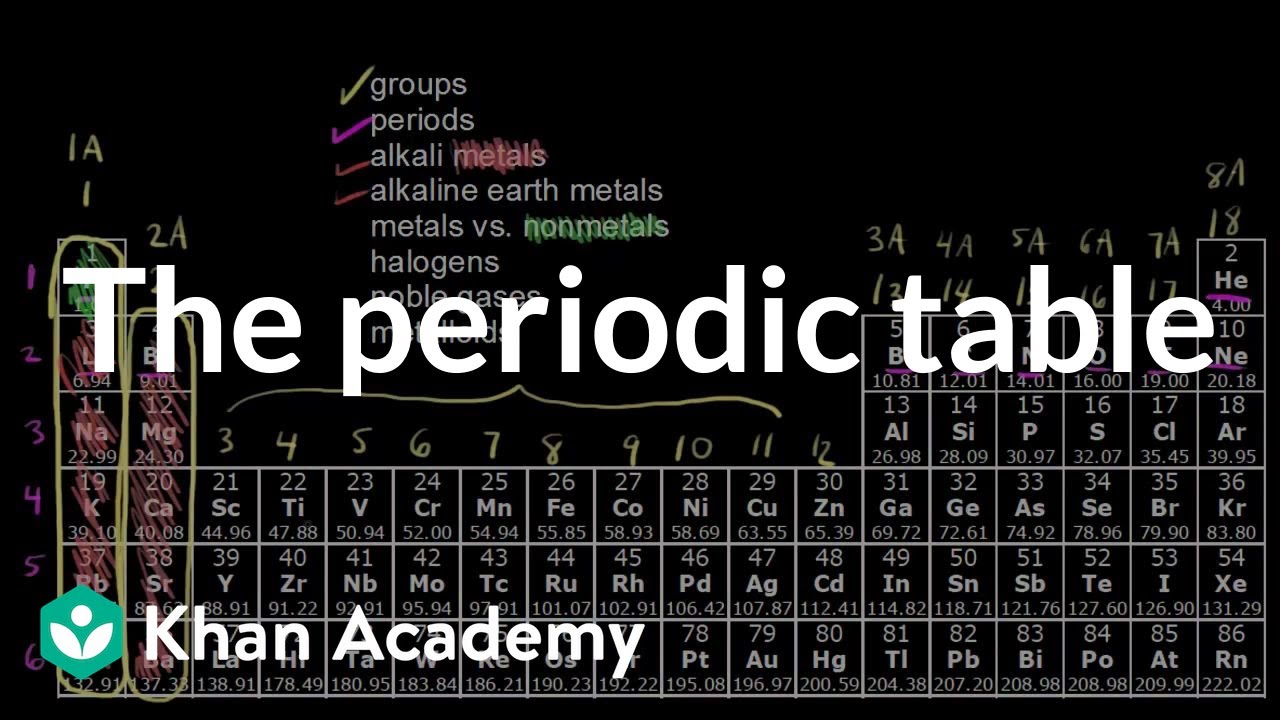
Definitions Of Groups Periods Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Halogens And Noble Gases How Metals Non Met Periodic Table Chemistry Element Chemistry

More Cheaty Revision Actual Xenon Compounds Electrons Element Chemistry Electron Configuration

Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry

Science Coverage How Many Valence Electrons Does Hydrogen H Have Electron Configuration Electrons Covalent Bonding

Alkali Metals Properties Periodic Table Ios App Chemistry Periodic Table App

Valence Electrons Definition Configuration Examples Electron Configuration Electrons Covalent Bonding

Electronegativity Teaching Chemistry High School Chemistry Class Notes
Comments
Post a Comment